This 12-word phrase is the master seed — your private keys all rolled up into one, easily managed format. All of your private keys and addresses are derived from it. The 12-words are just as useful. A tool for converting BIP39 mnemonic phrases to addresses and private keys. Enter your BIP39 phrase into the 'BIP39 Phrase' field, or press 'Generate Random Phrase'. You can save this page, turn off internet and generate private keys as lot as you wish.
Bitcoin Private Keys: Everything You Need To Know
Bitcoin Private Keys: Everything You Need To Know By: Sudhir Khatwani In: Bitcoin , Wallets Last Updated: What if you lost all of your bitcoins tomorrow? What would you do? If you dont own your private key, you dont own your bitcoins. Even the most knowledgeable man on Bitcoin says: The private key must remain secret at all times because revealing it to third parties is equivalent to giving them control over the bitcoins secured by that key. The private key must also be backed up and protected from accidental loss, because if its lost it cannot be recovered and the funds secured by it are forever lost, too. In my earlier guide on Bitcoin wallets , I have used two terms extensively-Private Address (or key) and Public Address (or key).These keys are what make Bitcoin the safest and most widely used cryptocurrency . Tounderstand private keys and public keys, let us look at an example. Consider a mailbox where you receive your physical mail. It has a unique and specific number (an address). If someone has to deliver you a letter, he/she must know your house/flat number to deliver it. And as the receiver, you have a private address (or key)to unlock the mailbox and collect your belongings. In real life, do you give your keys to someone unknown? You always keep track of your key and dont jeopardize the contents inside of your mailbox. Similarly, just like your house/flat number, anyone in the Bitcoin world can know your public address(Bitcoin address) to send you bitcoins. And to unlock (spend/send) those bitcoins, you would requireyour private address (or key)for which you need to take full responsibility, just like the keys of the mailbox. I feel that understanding the underlying technical aspect of keys is important so that your remain better informed and educated enoughContinue reading >>
How To Evaluate If This (or Any) Bitcoin Public Key / Private Key Combination Is Valid?
Let's say some software gave me the following combination: And let's say that for whatever reason, I want to test the validity: that the public key is a valid bitcoin address that can receive payments, and that the private key is valid for this particular public key What are my options to evaluate the validity of 1 and 2? Key encoding will be useful to give you a precise example. Are the values you are asking actually correct keys, or just made up strings? sr-gi Oct 19 at 18:14 Alright, it's WIF. sr-gi Oct 19 at 18:21 @sr-gi Not made up, some software gave them to me. (For others: WIF = wallet import format.) thanks_in_advance Oct 20 at 19:11 Yep, I got it. Actually I've proved that they match in my answer. sr-gi Oct 20 at 19:14 1) A Bitcoin address is between 25 and 34 characters long 2) the address always starts with a 1 (in this case) 3) an address can contain all alphanumeric characters, with the exceptions of 0, O, I, and l. (ref: ) Now here comes the hard part: The last four bytes of the address are the first four bytes of Sha256(Sha256(2,3,4...21th bytes of the address)) That is not a public key. That is an address, which is an encoding of the hash of a public key. that the public key is a valid bitcoin address that can receive payments, and You can check that the Bitcoin address is valid by decoding the Base58 Check Encoding of the address. When you decode the base58 string, you should have 25 hex bytes. The last 4 bytes are a checksum. They are the first 4 bytes of the double sha256 hash of the first 21 bytes of what you decoded. So you can hash those 21 bytes and make sure that they match the last 4 bytes. If they do, then the address is valid and coins can be sent to it. that the private key is valid for this particular public key Decode the private key to iContinue reading >>
Bitcoins
[ Back ] Bitcoins generate a 256-bit random key which is converted in a Wif (Wallet Interchange Format key), where there is a 256-bit private key and a 512-bit public key. It uses Elliptic Curve Ciphers (ECC) to sign for transactions: Private key: 2255cb6746a89fa0ce302a48147402437f7f069ffe507efb9deafa26bbd5b640Public key: 045e120534846e3c89d914c4720c9b86a156b7ec1384c0a60d5e285fcc631b81d1854c2ed552c900e698b351116b060166fd35da70ed67ba9380ba981a4a94504bWif: 5J5QdHdJnegdEm7cfGjr8HYeCaYYkckopT1mscea3Z6Mf34ESTHAddress: 16G8hmAgGon94vUkn7qhphPUr62nmBmgH3Signed: 493046022100ef802c450e51401392ca19401bf41792ca530e048bc34bec4b67c2bb656cef10022100ba2510d4a7ffc22d1f38beafdb52cadc53cafb3f10c3c370940a7e4b8b820e4501 41045e120534846e3c89d914c4720c9b86a156b7ec1384c0a60d5e285fcc631b81d1854c2ed552c900e698b351116b060166fd35da70ed67ba9380ba981a4a94504b With Bitcoins we create a 256-bit random for the private key, and then convert it to Wallet Interchange Format key (WiF) format, which is a Base-58 form for the random key. This is the format that is stored in the Bitcoin Wallet. For example a sample private key is: Private key: 5c04990cf2fb95ca8749d4021100ee98b0744e81a5ec00a2177aeaf4b29c00d3 We then convert this into WiF format (Base-58) to give: 5JWp4FM7sfAAE88DW3yvGF5mQyrsEXeWzXZn79bg61Vg8YMfJjA This can be stored in a Bitcoin wallet. Next we can take then private key and a hash value, and covert it into a useable Bitcoin address, such as: The format of the keys is defined below, where we create a 256-bit private key and convert this to a WiF private key. Next we generate a 512-bit public key, and then take a 160-bit RIPEM-160 hash and convert to a Bitcoin address: Bitcoins use Elliptic Curve Ciphers (ECC) with a 256-bit private key (and a 512-bit public key). If you want to know more abouContinue reading >>
How To Steal Bitcoins
This article is also available in French here . Every Bitcoin address is based on a secret key, from which the public key (associated to a Bitcoin address) is calculated. Once you have the private key for an address,you have the control of that address and can use it to transfer funds. This secret key is a 32-bytes unsigned integer. You can generate a lot of secret keys, calculate the public keys associated to them and see if they contain bitcoins.If its the case, you can transfer the money to an address you control, because you have the secret key. Such an attack is completely infeasible, because the private key space is really, really huge. There are 115792089237316195423570985008687907853269984665640564039457584007913129639936 secret keys available (1077). Oh, and they are all listed on directory.io ! Of course, this website is kind of a joke , and all is calculated on the fly when you request a specific page.It also shows the danger of entering your secret key on an unknown website, for example to see if it was compromised... However, we can bruteforce only a tiny fraction of this space, concentrating on secret keys with some distinctive features. This is what I will explain. I have made a script that tries every secret key, counting from 1. After some seconds, I found dozens of already used addresses, with private key smaller than 100 000 ! In particular, the 1EHNa6Q4Jz2uvNExL497mE43ikXhwF6kZm address (corresponding to the private key 1) was already used quite a lot, as 4 bitcoins already flowed through it. Brainwallet is a website that allow people to create private keys from a passphrase. It calculates the private key from the sha256 of the passphrase. By using a password dictionary, we can search for private keys corresponding to classic password that were alreContinue reading >>
Pete Corey - Generating Bitcoin Private Keys And Public Addresses With Elixir
Generating Bitcoin Private Keys and Public Addresses with Elixir Lately Ive been working my way through Mastering Bitcoin , implementing as many of the examples in the book in Elixir as I can. Ive been amazed at how well Elixir has fared with implementing the algorithms involved in working with Bitcoin keys and addresses. Elixir ships with all the tools required to generate a cryptographically secure private key and transform it into a public address string. Lets walk through the process step by step and build our our own Elixir module to generate private keys and public addresses. What are Private Keys and Public Addresses? A Bitcoin private key is really just a random two hundred fifty six bit number. As the name implies, this number is intended to be kept private. From each private key, a public-facing Bitcoin address can be generated. Bitcoin can be sent to this public address by anyone in the world. However, only the keeper of the private key can produce a signature that allows them to access the Bitcoin stored there. Lets use Elixir to generate a cryptographically secure private key and then generate its most basic corresponding public address so we can receive some Bitcoin! As I mentioned earlier, a Bitcoin private key is really just a random two hundred and fifty six bit number. In other words, a private key can be any number between 0 and 2^256. However, not all random numbers are created equally. We need to be sure that were generating our random number from a cryptographically secure source of entropy . Thankfully, Elixir exposes Erlangs :crypto.strong_rand_bytes/1 function which lets us easily generate a list of truly random bytes. Lets use :crypto.strong_rand_bytes/1 as the basis for our private key generator. Well start by creating a new PrivateKey moduleContinue reading >>
Phrase Generator Bitcoin Private Key
Why Do I Need A Public And Private Key On The Blockchain?
Why Do I Need a Public and Private Key on the Blockchain? When someone sends you cryptocoins over the Blockchain, they are actually sending them to a hashed version of whats known as the Public Key. There is another key which is hidden from them, that is known as the Private Key. This Private Key is used to derive the Public Key. You can know your own Private Key, and everyone else on the Blockchain knows their own Private Key, but the Private Key should not be shared with outsiders (that is, unless you want your cryptocurrencies to be stolen!). Both the Private Key and the Public Key are large integer numbers, but since these numbers are so large, they are usually represented using a separate Wallet Import Format (WIF) consisting of letters and numbers. The Private Key is the longer of the two, and is used to generate a signature for each blockchain transaction a user sends out. This signature is used to confirm that the transaction has come from the user, and also prevents the transaction from being altered by anyone once it has been issued. In short, you sign the cryptocurrencies you send to others using a Private Key. If someone were to obtain your private key, they would be able to send your cryptocurrencies to themselves, verifying that transaction with the Private Key in effect stealing from you! The Private Key is used to mathematically derive the Public Key, which (along with information about the network and a checksum)is then transformed with a hash function to produce the address that other people can see. You receive cryptocurrencies that others send to your address (which is a result of the hash of your public key and some additional information). At this point, you may be asking yourself, if a Public Key is derived from a Private Key, couldnt someone creContinue reading >>
Six Things Bitcoin Users Should Know About Private Keys
Six Things Bitcoin Users Should Know about Private Keys Private keys have been an integral component of Bitcoin since its first description in 2008. Wallet software often attempts to shield users from the need to understand what private keys are and how they work. Even so, most users eventually come face to face with private keys, too often with unpleasant results. A basic understanding of private keys can help prevent loss of funds and other mishaps, but it can also offer useful insights into how Bitcoin works. This guide outlines the most important private key concepts for using Bitcoin effectively. Although Bitcoin is best known as an electronic cash system , underneath it all runs a secure messaging system built on the Internet. Instead of relaying emails, texts, or web pages, the Bitcoin network processes value-transfer messages called transactions. Private keys play a central role in authenticating these messages and allowing users to identify each other. An example helps illustrate the problems that private keys solve. Imagine Alice wants to pay Bob using a coin with a face value of 1. Her plan is to create a transaction identifying Bob as the payee. After doing so, Alice plans to publish the transaction to the Bitcoin network. In using this system, Alice faces two fundamental problems: Alice needs a way to identify both herself and Bob in the transaction. She cant employ a trusted authority such as a government registry or email provider because that would create a central point of control and failure the very thing Bitcoin was created to eliminate. Alice needs a way to prevent others from changing her transaction and forging transactions in her name. Bitcoin solves both problems through a system called public key cryptography . This system uses two pieces of iContinue reading >>
Lets Enhance! How We Found @rogerkvers $1,000 Wallet Obfuscated Privatekey
Lets Enhance! How we found @rogerkvers $1,000 wallet obfuscated privatekey Part of the documentary where Roger Ver gives the details of the Bitcoin wallet. Before we even start: We do not know the journalists who recorded the interview and we do not know Roger Ver. Anyone who had access to this video could have retrieved the private key. We could have simply named this post How great QR code are and how we recovered one from almost nothing. But its much more interesting when the QR code is the key to a $1000 Bitcoin Cash wallet. Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, Dash, Neo Cryptocurrencies are all over and are moving fast. I have been following Bitcoin since 2013 (following doesnt mean buying), had to read Mastering Bitcoin 3 times to understand how each part of it really works and be able to explain it to someone else. Still, I cant keep up with the market, new cryptocurrencies, new forks, new ICOs everywhere, every day. Its easy to start using cryptocurrencies by following a tutorial online. Download a random wallet app, generate a random pair of keys and buy some crypto on a random exchange but the cryptocurrencies learning curve is difficult. If you dont fully understand how all parts of this work you should avoid cryptocurrencies. If you dont, you risk losing your money by falling in one of the many pitfalls. One of them, keeping your private key secure, is the subject of this post. The first rule of Crypto Club is: You do not share your privatekey. The most precious thing you have when you own cryptocurrencies is your private key. If you lose your private key, you lose your money. If someone gets access to your private key, you lose your money. Simple. With this real-world example will show you step by step how we recovered the private key of the $1000 Bitcoin wallet cContinue reading >>
4. Keys, Addresses - Mastering Bitcoin, 2nd Edition [book]
You may have heard that bitcoin is based on cryptography, which is a branch of mathematics used extensively in computer security. Cryptography means secret writing in Greek, but the science of cryptography encompasses more than just secret writing, which is referred to as encryption. Cryptography can also be used to prove knowledge of a secret without revealing that secret (digital signature), or prove the authenticity of data (digital fingerprint). These types of cryptographic proofs are the mathematical tools critical to bitcoin and used extensively in bitcoin applications. Ironically, encryption is not an important part of bitcoin, as its communications and transaction data are not encrypted and do not need to be encrypted to protect the funds. In this chapter we will introduce some of the cryptography used in bitcoin to control ownership of funds, in the form of keys, addresses, and wallets. Ownership of bitcoin is established through digital keys, bitcoin addresses, and digital signatures. The digital keys are not actually stored in the network, but are instead created and stored by users in a file, or simple database, called a wallet. The digital keys in a users wallet are completely independent of the bitcoin protocol and can be generated and managed by the users wallet software without reference to the blockchain or access to the internet. Keys enable many of the interesting properties of bitcoin, including decentralized trust and control, ownership attestation, and the cryptographic-proof security model. Most bitcoin transactions requires a valid digital signature to be included in the blockchain, which can only be generated with a secret key; therefore, anyone with a copy of that key has control of the bitcoin. The digital signature used to spend funds is alsContinue reading >>
Private Key - Bitcoin Wiki
This page contains sample addresses and/or private keys. Do not send bitcoins to or import any sample keys; you will lose your money. A private key in the context of Bitcoin is a secret number that allows bitcoins to be spent.Every Bitcoin wallet contains one or more private keys, which are saved in the wallet file.The private keys are mathematically related to all Bitcoin addresses generated for the wallet. Because the private key is the 'ticket' that allows someone to spend bitcoins, it is important that these are kept secure.Private keys can be kept on computer files, but in some cases are also short enough that they can be printed on paper. Some wallets allow private keys to be imported without generating any transactions while other wallets or services require that the private key be swept.When a private key is swept, a transaction is broadcast that sends the balance controlled by the private key to a new address in the wallet.Just as with any other transaction, there is risk of swept transactions to be double-spending. In contrast, bitcoind provides a facility to import a private key without creating a sweep transaction.This is considered very dangerous, and not intended to be used even by power users or experts except in very specific cases.Bitcoins can be easily stolen at any time, from a wallet which has imported an untrusted or otherwise insecure private key - this can include private keys generated offline and never seen by someone else [1] [2] . In Bitcoin, a private key is usually a 256-bit number (some newer wallets may use between 128 and 512 bits), which can be represented one of several ways.Here is a private key in hexadecimal - 256 bits in hexadecimal is 32 bytes, or 64 characters in the range 0-9 or A-F. E9873D79C6D87DC0FB6A5778633389_SAMPLE_PRIVATEContinue reading >>
Bitcoin Public And Private Keys
There is more to a bitcoin wallet than just the address itself. It also contains the public and private key for each of your bitcoin addresses. Your bitcoin private key is a randomly generated string (numbers and letters), allowing bitcoins to be spent. A private key is always mathematically related to the bitcoin wallet address, but is impossible to reverse engineer thanks to a strong encryption code base. If you dont back up your private key and you lose it, you can no longer access your bitcoin wallet to spend funds. As mentioned, there is also a public key. This causes some confusion, as some people assume that a bitcoin wallet address and the public key are the same. That is not the case, but they are mathematically related. A bitcoin wallet address is a hashed version of your public key. Every public key is 256 bits long sorry, this is mathematical stuff and the final hash (your wallet address) is 160 bits long. The public key is used to ensure you are the owner of an address that can receive funds. The public key is also mathematically derived from your private key, but using reverse mathematics to derive the private key would take the worlds most powerful supercomputer many trillion years to crack. Besides these key pairs and a bitcoin wallet address, your bitcoin wallet also stores a separate log of all of your incoming and outgoing transactions. Every transaction linked to your address will be stored by the bitcoin wallet to give users an overview of their spending and receiving habits. Last but not least, a bitcoin wallet also stores your user preferences. However, these preferences depend on which wallet type youre using and on which platform. The Bitcoin Core client, for example, has very few preferences to tinker around with, making it less confusing forContinue reading >>
Private Key. All About Cryptocurrency - Bitcoin Wiki
A private key in the context of Bitcoin is a secret number that allows bitcoins to be spent. Every Bitcoin address has a matching private key, which is saved in the wallet file of the person who owns the balance. The private key is mathematically related to the Bitcoin address, and is designed so that the Bitcoin address can be calculated from the private key, but importantly, the same cannot be done in reverse. Because the private key is the 'ticket' that allows someone to spend bitcoins, it is important that these are kept secure. Private keys can be kept on computer files, but they are also short enough that they can be printed on paper. An example of a utility that allows extraction of private keys from your wallet file for printing purposes is pywallet. In order to create a transaction with a private key, it must be available to a program or service that allows entry or importing of private keys. Some wallets allow the private key to be imported without generating any transactions while other wallets or services require that the private key be swept. When a private key is swept, a transaction is broadcast that sends the entire balance held by the private key to another address in the wallet or securely controlled by the service in question. An example of private key sweeping is the method used on MtGox's Add Funds screen and BIPS Import screen. Just as with any other deposit, there is risk of double-spending so funds are deposited to the MtGox account after a six-confirmation wait (typically one hour). In contrast BlockChain .info's My Wallet service and Bitcoin-QT each provide a facility to import a private key without creating a sweep transaction [1] . In Bitcoin, private key is a 256-bit number, which can be represented one of several ways. Here is a private keContinue reading >>
How To Import And Export Bitcoin Private Keys
How to Import and Export Bitcoin Private Keys How to Import and Export Bitcoin Private Keys This guide was originally written with Bitcoin (BTC) in mind. The same steps apply for Bitcoin Cash (BCH) wallets. Just make sure you are dealing with the keys for the correct currencys wallet(s) before proceeding. Before getting started with importing your wallets private keys , lets clarify three important definitions. Backup: A filecontaining a wallets private key information. Backups can be exported from a wallet or imported to a wallet. Export:The process of creating a file containing a wallets private key data. Exported keys can be imported to a new/different wallet to give access to the Bitcoins associated with the exported private key(s). Import:The process of gaining control of Bitcoins via an exported backup. Wallets can import private keys via text files or QR code scanning. Bitcoins are not stored locally on your phone or laptop. They are stored on the blockchain and you use a Bitcoin wallet to access the coins for sending/receiving the cryptocurrency. This means if you lose your phone or buy a new laptop you can access your bitcoin by importing your key(s) from a previously exported backup. With a backup, you are able to recover your bitcoin at any time by importing the private keys associated with that wallet from the backup. This is why it is imperative that users take the time to createa backup of their wallet before adding bitcoin to it. For more on creating a backup, please see our Bitcoin.com wallet guide . If you have not already done so, please go ahead and backup your wallet. This process is covered in detail in the guide on how to use the Bitcoin.com wallet . If you do not backup your wallet and store this information somewhere safe you run the risk of losContinue reading >>

What's A Bitcoin Address? Public Keys, Private Keys, And Addresses Explained
One of the things I get asked all the time is what is a bitcoin address?. Theres the full technical answer for someone who wants to build bitcoin technologies, but theres a lot less to know to bea user of bitcoin nowadays. For example, I bet you didnt know that email runs on a protocol called SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) which plays a similar role in email that the bitcoin protocol does in transferring bitcoin (although with some key differences). But if I asked you to fire off an email to [email protected] you could have something ready to send in less than a minute. Sending bitcoin is a similar level of complexity, only you dont need to write a message to send bitcoin. Even Fluffy can send an email with her eyes closed. A lot of people seem to worry about learning the complex mathematics behind the bitcoin protocol before buying and using bitcoin. This might have been true pre-2014 before hoards of startups set out to make bitcoin accessible, but today its simply not the case. So Im going to give you the basic information you need to know to be a userof bitcoin, but not a mathematical expert. So lets get started! A bitcoin address is one of the key concepts that make the currency and the blockchain work. It isnt quite as straightforward to define or explain as an email address. You first need to know about two other parts of bitcoin in order to see how the address fits into the picture: a private key and a public key. The main difference is that you dont use the same address to send bitcoin as you do to receive it. Instead, there are three key terms to know: Private key : a 64 character long code using any combination of the letters A-F and the numbers 1-9. You can see an example of a private key on the image above.This is what you use to send money out of youContinue reading >>

What Is A Bitcoin Private Key?
Phrase Generator Bitcoin Private Key Free
What is a Bitcoin Private Key, How to Use It, Keep it Safe! Last updated on October 13th, 2017 at 07:08 pm What is Bitcoin ? Bitcoin is a digital currency and a payment system that was introduced as an open source software by Satoshi Nakamoto who developed it. It utilizes peer to peer technology since money can be transferred from one individual to another directly without the involvement of a central bank. All payments are usually recorded on a public ledger. Individuals using software such as wallet software can get to send and receive bitcoins electronically through a PC, smartphone or web app. What is a bitcoin private key? Bitcoin private key is a secret number generated to allow individuals to spend their bitcoins. When users are issued with a bitcoin address, they are also issued with a bitcoin private key. It is usually a 256 bit number and since it is the golden ticket that allows an individual to spend his or her bitcoins, it needs to be kept safe and securely. An example of a bitcoin private key is16qT2iLQ7d5MiEkKWYau6mfRNHUFZ3NzHz. This is our bitcoin private key, by the way. A private key can be used to accept accept, sell and donate bitcoin. Many charities are now accepting bitcoins . One of the ways one can keep a bitcoin private key safely is by storing it in their computers in a disk that it encrypted. Since the bitcoin private key is short, other can get to print it on a piece of paper. This can be accomplished by using pywallet. Pywallet is a utility developed using python that allows users to extract private keys from their wallet files. The extracted files can then be printed on to a small piece of paper using a printer. RELATED: What is a Bitcoin Wallet and How to Get One In order to make a transaction, the user should have availability to a toolContinue reading >>
Bitcoin & Cryptology
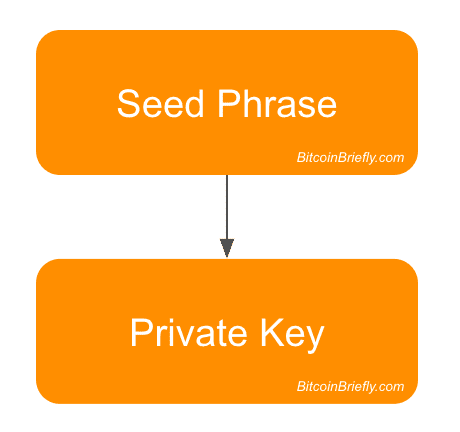
Let’s explore some more about the Seed and the pairing of Private Keys, Public Keys and Bitcoin Addresses. Our Electrum Wallet was generated using some random words called the Seed. But what exactly is this Seed, and what does it do? At the heart of Bitcoin is advanced Cryptology software that is used to encrypt and decrypt Bitcoin Wallets and Bitcoin Transactions. When you first create your Wallet, the Seed is picked up by the Wallet’s advanced Cryptology software to generate a number of unique items. The random words and letter placement in the seed is used by the encryption algorithms, to create encryption patterns and Keys that are unique to your Wallet.[
First, your Wallet’s main datafile, which stores details of your Bitcoin transactions is created and encrypted. As the Blockchain Public Ledger holds details of every single Bitcoin Transaction ever made, all transactions from your Wallet will also exist in the Blockchain Public Ledger. Next, matching pairs of Private Keys and Public Keys will be created, along with some unique Bitcoin Addresses that are matched to these keys. You need a supply of Bitcoin Addresses in order to send or receive Bitcoin into your Wallet. And every Wallet can create an unlimited number of unique Addresses.
Private Keys and Public Keys
Each Bitcoin Address is directly linked to a pair of matching keys, the Private Key, and the Public Key. The “Private Key”, must remain securely on your own Wallet, as it is used to encrypt and authorize transactions leaving your Wallet. Never, for any reason show anyone what your Private Keys are, as this makes your Wallet vulnerable to cyber-crime and potential theft. If anyone found out what your Private Keys were, they could potentially steal Bitcoins from your Wallet, in much the same way that they could if they stole your Seed. The other Key is the Public Key. This matches up with your Private Key, to form a matching pair, a bit like non-identical twins.
Next we have the Bitcoin Address itself. Every Bitcoin Transaction you make from your Wallet generally uses a completely new and unique Bitcoin Address, which helps retain your anonymity and protects your wallet. The Bitcoin address is a mathematically related shortened version of your Public Key, created using a technique called hashing. So in summary, a bitcoin address is a mathematically related and shortened version of your public key, which itself is mathematically related to your much larger and more complex Private key. Your Private Key creates your Public Keys, authorizes transactions leaving your Wallet, and proves ownership of your transactions. I did mention Bitcoin was complicated, didn’t I?
When Bitcoin transactions are decrypted by the Miners, for inclusion into the Blockchain Public Ledger, the included Public Key and Bitcoin Addresses identifies the transaction as either coming from your Wallet, or being sent to your Wallet. You can view your Private Keys inside your Wallet, but you don’t need to worry about them too much for day-to-day use. The pairing of public and private keys, when transacting in Bitcoin, is handled automatically by your Wallet. If you want to learn more about the Seed, Bitcoin Addresses, and Public or Private Keys, check the Webpage for this episode and follow the links to more reading.